Capsanthin is a natural pigment found in various types of chili peppers, particularly in red peppers. It belongs to a class of pigments called carotenoids, which are responsible for the vibrant red, orange, and yellow colors in many fruits and vegetables. Here are some key points about capsanthin:
Natural food coloring: Capsanthin is commonly used as a natural food coloring agent. It imparts a bright red color to food and beverages and is often used in products like sauces, marinades, beverages, and confectionery.
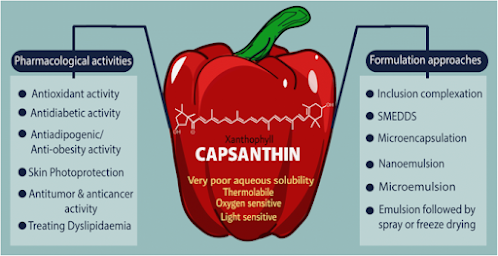
Antioxidant properties: Capsanthin, like other carotenoids, has antioxidant properties. Antioxidants help protect cells from damage caused by harmful molecules called free radicals, which can contribute to oxidative stress and various health issues.
Eye health support: Carotenoids, including capsanthin, are known to have benefits for eye health. They are concentrated in the macula of the eye and help filter harmful blue light and support the overall health of the retina.
Anti-inflammatory potential: Some research suggests that capsanthin may have anti-inflammatory properties. It may help reduce inflammation and oxidative stress in the body, potentially contributing to overall health and well-being.
Potential health benefits: Although more research is needed, capsanthin has been studied for potential health benefits, including its role in cardiovascular health, immune support, and its potential anticancer properties.
Dietary sources: Capsanthin is primarily found in red chili peppers, such as cayenne pepper, paprika, and red bell peppers. The concentration of capsanthin varies depending on the pepper variety and its ripeness.
It's important to note that while capsanthin is generally considered safe for consumption as a food pigment, specific supplementation with capsanthin as a dietary supplement is not widely available or studied. As always, it's recommended to consult with a healthcare professional or a registered dietitian for personalized advice and guidance related to your specific health needs and conditions.



Comments
Post a Comment