 | ||
| Chrysin for Testosterone |
 |
| Chrysin and Estrogenic Effects |
Chrysin is a naturally occurring flavonoid compound found in various plants, including passionflowers, honeycomb, and some fruits and vegetables. It has gained attention for its potential health benefits and is being explored for its various properties. This article provides an overview of chrysin, its sources, potential health benefits, and current understanding based on available research.
Sources of Chrysin:
Chrysin can be found in plants such as passionflowers (Passiflora spp.), propolis (a resin-like substance produced by bees), honey, and certain fruits and vegetables. It is also available in the form of dietary supplements.
Potential Health Benefits of Chrysin:
Antioxidant Activity:
Chrysin exhibits antioxidant properties, which means it can help neutralize harmful free radicals in the body. Antioxidants play a crucial role in protecting cells from oxidative damage and promoting overall health.
Anti-Inflammatory Effects:
Some studies suggest that chrysin may possess anti-inflammatory properties. It may help inhibit certain inflammatory molecules, potentially contributing to reduced inflammation in the body. However, further research is needed to establish the extent of its anti-inflammatory effects and its potential applications.
Estrogenic Effects:
Chrysin has been investigated for its ability to interact with estrogen receptors in the body. It may exhibit weak estrogenic activity, which could have implications for hormone-related conditions. However, more research is required to fully understand its effects on estrogen receptors and its potential applications in this area.
Anticancer Potential:
Chrysin has attracted attention for its potential anticancer properties. Studies in cell cultures and animal models have shown that it may have antiproliferative effects, meaning it can inhibit the growth of cancer cells. However, more research, including human clinical trials, is necessary to determine its efficacy and safety as an anticancer agent.
Current Understanding and Limitations:
It is important to note that the research on chrysin is still in its early stages, and the available studies have been predominantly conducted in laboratory settings or on animal models. Human studies are limited, and more research is needed to better understand the potential health benefits and therapeutic applications of chrysin.
Furthermore, chrysin has poor bioavailability, which means it is not easily absorbed and utilized by the body when consumed orally. This can limit its effectiveness as a standalone supplement. Researchers are exploring various delivery methods and formulations to improve its bioavailability.
Conclusion:
Chrysin, a flavonoid compound found in certain plants, exhibits potential health benefits such as antioxidant and anti-inflammatory activity. It has also been investigated for its estrogenic effects and potential anticancer properties. However, the current understanding is based on limited research, and more studies, particularly human clinical trials, are required to validate its efficacy, safety, and potential applications. Individuals interested in using chrysin as a dietary supplement should consult with a healthcare professional for guidance, especially if they have underlying health conditions or are taking medications.
Disclaimer: This article is for informational purposes only and should not be considered as medical advice. Consult with a healthcare professional before starting any new supplements or treatments.
FAQ:
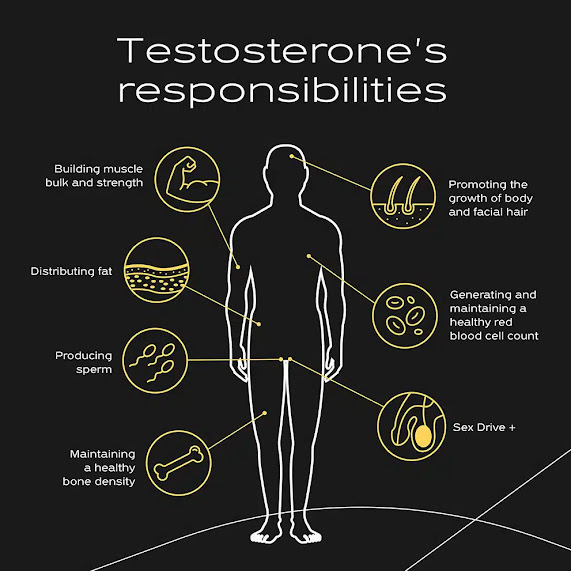
(1) Will Chrysin increase testosterone and improve bodybuilding?
Chrysin has been studied for its potential effects on testosterone levels and its impact on bodybuilding. However, it's important to note that the research on chrysin's ability to increase testosterone and enhance bodybuilding performance is limited and inconclusive.
Chrysin is believed to inhibit an enzyme called aromatase, which converts testosterone into estrogen. By inhibiting aromatase, chrysin may potentially help maintain higher levels of testosterone in the body. However, studies investigating the direct effects of chrysin on testosterone levels in humans have yielded mixed results, with some studies showing minimal or no significant impact on testosterone.
Furthermore, even if chrysin does have the ability to affect testosterone levels, it may have limited practical relevance for bodybuilding and athletic performance. Testosterone is just one of several factors influencing muscle growth and athletic performance. Other factors, including proper training, nutrition, rest, and overall hormone balance, play significant roles as well.
It's also important to consider the challenge of achieving sufficient chrysin levels in the body through oral supplementation. Chrysin has poor bioavailability, meaning it is not easily absorbed and utilized by the body when taken orally. This can limit its effectiveness as a standalone supplement.
If you are interested in using chrysin or any other supplement for bodybuilding purposes, it is advisable to consult with a healthcare professional or a registered dietitian who specializes in sports nutrition. They can provide personalized advice, consider your individual needs and goals, and recommend evidence-based strategies to support your bodybuilding efforts.
Chrysin is a naturally occurring flavonoid compound found in various plants. It belongs to a class of phytochemicals called flavones. It is commonly found in plants such as passionflowers (Passiflora spp.), propolis (a resin-like substance produced by bees), honey, and certain fruits and vegetables.Chrysin has attracted attention due to its potential health benefits and is the subject of ongoing scientific research. It is known for its antioxidant properties, which means it can help neutralize harmful free radicals in the body. Antioxidants are important for protecting cells from oxidative damage and promoting overall health.Chrysin has also been studied for its potential anti-inflammatory effects. It may help reduce inflammation in the body by inhibiting certain inflammatory molecules. Additionally, chrysin has been investigated for its interaction with estrogen receptors, which may have implications for hormone-related conditions.It's worth noting that the research on chrysin is still limited, and much of the available information comes from laboratory studies or animal models. Human studies are relatively scarce, and more research is needed to fully understand the potential health benefits and therapeutic applications of chrysin.Chrysin is available in the form of dietary supplements. However, it's important to consult with a healthcare professional before using chrysin supplements, especially if you have any underlying health conditions or are taking medications. They can provide personalized advice and help you make informed decisions regarding its use.
Chrysin is a natural flavonoid compound found in certain plants, such as passionflower and honeycomb. It has gained attention for its potential health benefits and is available as a dietary supplement. However, it's important to note that the scientific evidence regarding the effectiveness and safety of chrysin is limited, and more research is needed to fully understand its potential benefits. Here are some of the uses and purported benefits associated with chrysin:Antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties: Chrysin is believed to possess antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties, which may help protect cells from oxidative stress and reduce inflammation in the body. These properties are generally associated with overall health and well-being.
Testosterone regulation: Chrysin has been studied for its potential effects on testosterone levels. Some research suggests that chrysin may inhibit the conversion of testosterone to estrogen by blocking the aromatase enzyme. However, the evidence is limited, and more studies are needed to confirm the effectiveness of chrysin in this regard.
Anti-anxiety and sleep support: Chrysin has been investigated for its potential anxiolytic (anti-anxiety) and sedative effects. Some studies in animal models have shown promising results, but human studies are lacking. It is thought that chrysin may act on certain receptors in the brain involved in anxiety and sleep regulation.
Cancer research: Chrysin has been studied for its potential anticancer properties. Some in vitro (test tube) and animal studies have suggested that chrysin may have anti-proliferative effects on certain cancer cells and may help inhibit tumor growth. However, more research, including human studies, is necessary to determine its efficacy and safety in cancer prevention or treatment.It's important to note that chrysin's bioavailability (ability to be absorbed and utilized by the body) is relatively low, and it can be quickly metabolized and eliminated from the body. This may limit its effectiveness when taken orally as a supplement.If you're considering using chrysin as a dietary supplement, it's advisable to consult with a healthcare professional or a registered dietitian. They can provide personalized guidance and help you make informed decisions based on your individual health needs and goals.
(4) What are some food sources of Chrysin?
Chrysin is a flavonoid compound found naturally in various plants. While it is not abundant in everyday foods, here are some common food sources that may contain small amounts of chrysin:
Passionflowers: Chrysin is most notably found in passionflower plants (Passiflora spp.). Consuming passionflower tea or extracts may provide a small amount of chrysin.
Honey: Certain types of honey, particularly honey made from nectar collected from plants like passionflowers, may contain traces of chrysin. However, the levels can vary depending on the specific source and processing methods.
Propolis: Propolis, a resin-like substance produced by bees, is sometimes used in traditional medicine. It may contain chrysin along with other flavonoids. Propolis can be found in health food stores or purchased directly from beekeepers.
Some fruits and vegetables: While the chrysin content in fruits and vegetables is generally low, certain plant-based foods may contain small amounts. Examples include celery, parsley, chamomile, and some types of citrus fruits.
It's important to note that the chrysin content in these food sources is typically quite low, and it may not provide significant levels of chrysin for therapeutic purposes. If you are considering using chrysin for specific health benefits, dietary supplements that provide concentrated chrysin are often preferred.
As with any dietary changes or supplementation, it's advisable to consult with a healthcare professional or a registered dietitian before making significant modifications to your diet or using chrysin supplements. They can provide personalized advice and help you make informed decisions based on your individual needs and health status.





Comments
Post a Comment