Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) is a hormonal sickness that impacts many women of reproductive age. While there may be no remedy for PCOS, sure nutraceuticals (herbal compounds with capacity health benefits) may additionally assist manipulate its signs. It's crucial to word that nutraceuticals should be used beneath the steering of a healthcare professional. Here are some nutraceuticals that have been studied for their potential benefits in PCOS:
PCOS supplements
Inositol: Inositol is a type of B vitamin that comes in two forms: myo-inositol (MI) and d-chiro-inositol (DCI). It has been shown to improve insulin sensitivity and regulate menstrual cycles in women with PCOS. Inositol supplementation may also help reduce hirsutism (excessive hair growth) and improve fertility.
N-acetylcysteine (NAC): NAC is an antioxidant that has shown promise in PCOS management. It helps improve insulin sensitivity, reduce oxidative stress, and regulate menstrual cycles. NAC may also help improve fertility in women with PCOS.
Omega-3 Fatty Acids: Omega-3 fatty acids, particularly eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA) and docosahexaenoic acid (DHA), have anti-inflammatory properties and may help reduce insulin resistance, regulate menstrual cycles, and improve lipid profiles in women with PCOS. These fatty acids can be obtained from fish oil supplements or by consuming fatty fish like salmon, sardines, and mackerel.
Chromium: Chromium is a mineral that plays a role in glucose metabolism. It may help improve insulin sensitivity and reduce insulin resistance in women with PCOS. However, it is important to note that chromium supplementation should be used with caution and under the guidance of a healthcare professional.
Vitamin D: Many women with PCOS have been found to have vitamin D deficiency. Vitamin D supplementation may help improve insulin sensitivity, regulate menstrual cycles, and reduce inflammation in women with PCOS. However, it is important to have your vitamin D levels checked and consult with a healthcare professional for appropriate dosage.
Cinnamon: Cinnamon has been studied for its potential benefits in PCOS. It may help improve insulin sensitivity, regulate menstrual cycles, and reduce inflammation. However, more research is needed to establish its efficacy and optimal dosage.
PCOS is becoming more common nowadays. The prevalence of PCOS is estimated to be 1 in 10 women of reproductive age worldwide. This means that about 10% of women between the ages of 15 and 44 have PCOS.
There are a few reasons why PCOS may be becoming more common. One reason is that obesity is a major risk factor for PCOS, and obesity is becoming more common in the world. Another reason is that we are better at diagnosing PCOS now than we were in the past.
PCOS is a complex disorder, and there is no one-size-fits-all treatment. However, there are several things that women with PCOS can do to manage their symptoms and improve their health. These include:
- Losing weight
- Eating a healthy diet
- Exercising regularly
- Taking medication
- Managing stress
If you think you may have PCOS, it is important to see a doctor for diagnosis and treatment. With the right care, women with PCOS can live healthy and fulfilling lives.
Here are some additional reasons why PCOS may be becoming more common:
- Changes in diet and lifestyle: The Western diet, which is high in processed foods, sugar, and saturated fat, is thought to contribute to the development of PCOS. Additionally, women who are more sedentary are at increased risk of PCOS.
- Environmental factors: Some studies have suggested that exposure to certain environmental chemicals, such as pesticides, may increase the risk of PCOS.
- Genetics: PCOS is a complex disorder that is influenced by both genetics and environmental factors. If you have a family history of PCOS, you are more likely to develop the condition yourself.
If you are concerned that you may have PCOS, it is important to see a doctor for diagnosis and treatment. With the right care, women with PCOS can live healthy and fulfilling lives.
What is PCOS? What causes PCOS?
PCOS is caused by an imbalance of hormones in the body. The ovaries produce too much of the male hormone androgen, which can lead to the symptoms of PCOS.
The exact cause of PCOS is unknown, but there are several factors that may contribute to the development of the condition, including:
Genetics: PCOS is thought to be a genetic condition, meaning that it can be passed down from parents to children.
Obesity: Women who are overweight or obese are more likely to develop PCOS.
Insulin resistance: Insulin is a hormone that helps the body use glucose for energy. Women with PCOS are often insulin resistant, meaning that their bodies do not respond to insulin as well as they should.
The symptoms of PCOS can vary from woman to woman. Some of the most common symptoms include:
Irregular menstrual cycles: Women with PCOS may have irregular menstrual cycles, or they may not have periods at all.
Excess hair growth: Women with PCOS may have excess hair growth on their face, chest, back, and other areas of the body.
Difficulty getting pregnant: Women with PCOS may have difficulty getting pregnant.
Weight gain: Women with PCOS are more likely to be overweight or obese.
Acne: Women with PCOS may have acne.
Thinning hair: Women with PCOS may experience thinning hair on their heads.
PCOS can be diagnosed by a doctor based on a woman's symptoms and medical history. There are no specific tests for PCOS, but doctors may order blood tests to check hormone levels and insulin resistance.
There is no cure for PCOS, but there are treatments that can help manage the symptoms. Treatment options for PCOS include:
Weight loss: Losing weight can help to improve the symptoms of PCOS.
Birth control pills: Birth control pills can help to regulate menstrual cycles and reduce excess hair growth.
Metformin: Metformin is a medication that can help to improve insulin resistance.
Other medications: Other medications, such as spironolactone, may be used to treat the symptoms of PCOS.
Women with PCOS should see their doctor regularly to monitor their symptoms and make sure that they are getting the right treatment. With proper treatment, women with PCOS can live healthy and fulfilling lives.
PCOS and PCOD
Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) and polycystic ovary disease (PCOD) are terms that are often used interchangeably, but they are not actually the same thing.
PCOS is a complex disorder that is caused by a combination of genetic and environmental factors. It is characterized by irregular menstrual cycles, excess hair growth, and difficulty getting pregnant.
PCOD, on the other hand, is a condition in which the ovaries produce many immature or partially mature eggs. This can lead to irregular menstrual cycles but does not necessarily affect fertility.
In other words, PCOD is a condition that can lead to PCOS, but not everyone with PCOD will develop PCOS.
The main difference between PCOS and PCOD is that PCOS is a syndrome, while PCOD is a disease. A syndrome is a group of symptoms that often occur together, while a disease is a specific condition that has a known cause.
PCOS is a syndrome because it is a group of symptoms that can occur together, but there is no single known cause. PCOD, on the other hand, is a disease because it is a specific condition that has a known cause, which is the presence of many immature or partially mature eggs in the ovaries.
It is important to note that the terms PCOD and PCOS are often used interchangeably, even by healthcare professionals. However, it is important to be aware of the difference between the two conditions.
Natural Remedies for PCOS
There is no one-size-fits-all cure for polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS), but there are several natural remedies that can help to manage the symptoms. These include:
Diet and exercise: Making healthy changes to your diet and exercise routine can help to improve insulin sensitivity, reduce inflammation, and lose weight. Some foods that are good for PCOS include leafy green vegetables, fatty fish, nuts, and seeds. Exercises that are good for PCOS include yoga, Pilates, and weight lifting.
Herbs and supplements: There are several herbs and supplements that are helpful for PCOS, including inositol, cinnamon, and Vitex. However, it is important to talk to your doctor before taking any supplements, as some can interact with medications.
Stress management: Stress can worsen the symptoms of PCOS, so it is important to find ways to manage stress. Some helpful stress management techniques include yoga, meditation, and deep breathing exercises.
Sleep hygiene: Getting enough sleep is essential for overall health, and it can also help to improve the symptoms of PCOS. Aim for 7-8 hours of sleep per night.
If you are struggling with PCOS, it is important to talk to your doctor. They can help you to develop a treatment plan that is right for you.
Here are some additional tips for managing PCOS naturally:
Avoid processed foods: Processed foods are often high in sugar, unhealthy fats, and calories. These can all worsen the symptoms of PCOS.
Eat plenty of fiber: Fiber can help to regulate blood sugar levels and reduce inflammation. Good sources of fiber include fruits, vegetables, and whole grains.
Drink plenty of water: Staying hydrated is important for overall health, and it can also help to improve the symptoms of PCOS. Aim to drink 8-10 glasses of water per day.
Manage your stress: Stress can worsen the symptoms of PCOS, so it is important to find ways to manage stress. Some helpful stress management techniques include yoga, meditation, and deep breathing exercises.
It is important to remember that there is no one-size-fits-all approach to managing PCOS. What works for one person may not work for another. It is important to find what works best for you and to be patient and persistent.
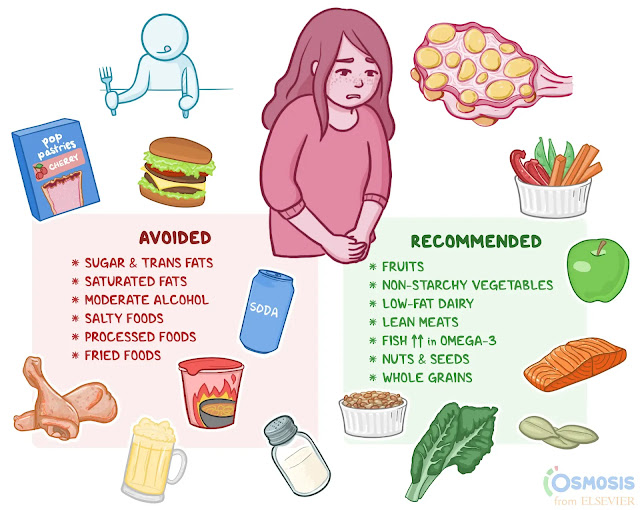
Diet for PCOS / PCOS Diet
There is a specific diet that can help manage PCOS. This diet is called the Mediterranean diet. The Mediterranean diet is a healthy diet that is rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and healthy fats. It is also low in processed foods, sugary drinks, and saturated and unhealthy fats.
The Mediterranean diet has been shown to help improve insulin sensitivity and reduce androgen levels. This can help to manage the symptoms of PCOS, such as weight gain, irregular periods, and infertility.
Here are some of the foods that are recommended for the Mediterranean diet:
Fruits: All fruits are good for people with PCOS, but some of the best fruits for PCOS include berries, citrus fruits, and apples.
Vegetables: All vegetables are good for people with PCOS, but some of the best vegetables for PCOS include leafy greens, cruciferous vegetables, and tomatoes.
Whole grains: Whole grains are a good source of fiber, which can help to regulate blood sugar levels. Some good whole grains for PCOS include brown rice, quinoa, and whole wheat pasta.
Healthy fats: Healthy fats, such as olive oil, avocados, and nuts, can help to improve insulin sensitivity and reduce inflammation.
Lean protein: Lean protein, such as fish, chicken, and beans, can help you feel full and satisfied.
Here are some of the foods that should be avoided on the Mediterranean diet:
Processed foods: Processed foods are high in unhealthy fats, sugar, and salt. They can also be high in calories, which can lead to weight gain.
Sugary drinks: Sugary drinks, such as soda, juice, and sweetened tea, are high in calories and sugar. They can also lead to weight gain and insulin resistance.
Saturated and unhealthy fats: Saturated and unhealthy fats, such as those found in red meat, processed meats, and fried foods, can raise cholesterol levels and increase the risk of heart disease.
If you are considering following the Mediterranean diet for PCOS, it is important to talk to your doctor first. They can help you create a plan that is right for you and your individual needs.
Here are some additional tips for following the Mediterranean diet for PCOS:
Make gradual changes: Don't try to change your entire diet overnight. Start by making small changes, such as adding more fruits and vegetables to your meals.
Be patient: It takes time to adjust to a new diet. Don't get discouraged if you don't see results right away. Just keep at it, and you will eventually see the benefits.
Find a support system: Having a support system can help you stay on track. Find friends or family members who are also following the Mediterranean diet, or join a support group online or in your community.
The Mediterranean diet is a healthy diet that can help manage PCOS. If you are considering following this diet, talk to your doctor first. They can help you create a plan that is right for you and your individual needs.
FAQs:
(1) How to get rid of PCOS?
Lifestyle changes: Making lifestyle changes, such as losing weight, eating a healthy diet, and exercising regularly, can help to improve insulin sensitivity and reduce androgen levels.
Medication: Medications, such as metformin and spironolactone, can help to improve insulin sensitivity and reduce androgen levels. These medications can also help to regulate your menstrual cycle and reduce the risk of complications, such as diabetes and heart disease.
Surgery: In some cases, surgery may be an option for women with PCOS who are not able to get pregnant with other treatments. Surgery can help to remove cysts from the ovaries and improve ovulation.
If you are diagnosed with PCOS, it is important to work with your doctor to develop a treatment plan that is right for you. The goal of treatment is to manage your symptoms and reduce your risk of complications.
It is important to note that there is no one-size-fits-all treatment for PCOS. The best treatment for you depends on your symptoms and medical history.
Here are some additional tips that may help you manage PCOS:
See your doctor regularly: It is important to see your doctor regularly to monitor your condition and make sure that your treatment plan is working.
Track your symptoms: Keeping track of your symptoms can help you to identify triggers and make sure that your treatment plan is effective.
Be patient: Finding the right treatment for PCOS may take some time. Be patient and work with your doctor to find a treatment plan that is right for you.
References:





Comments
Post a Comment